1.2 What is an algorithm¶
1.2.1 Definition of an algorithm¶
An algorithm is a set of instructions or steps to solve a specific problem within a finite amount of time. It has the following characteristics:
- The problem is clearly defined, including unambiguous definitions of input and output.
- The algorithm is feasible, meaning it can be completed within a finite number of steps, time, and memory space.
- Each step has a definitive meaning. The output is consistently the same under the same inputs and conditions.
1.2.2 Definition of a data structure¶
A data structure is a way of organizing and storing data in a computer, with the following design goals:
- Minimize space occupancy to save computer memory.
- Make data operations as fast as possible, covering data access, addition, deletion, updating, etc.
- Provide concise data representation and logical information to enable efficient algorithm execution.
Designing data structures is a balancing act, often requiring trade-offs. If you want to improve in one aspect, you often need to compromise in another. Here are two examples:
- Compared to arrays, linked lists offer more convenience in data addition and deletion but sacrifice data access speed.
- Compared with linked lists, graphs provide richer logical information but require more memory space.
1.2.3 Relationship between data structures and algorithms¶
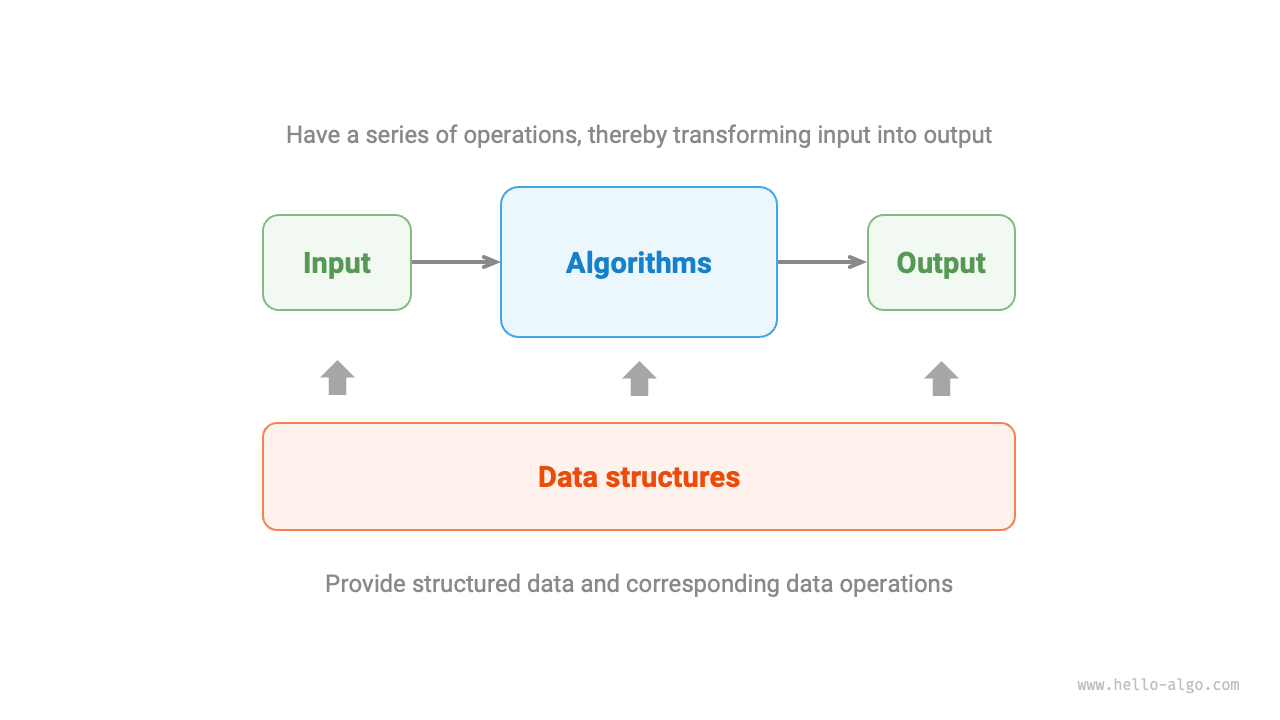
As shown in Figure 1-4, data structures and algorithms are highly related and closely integrated, specifically in the following three aspects:
- Data structures are the foundation of algorithms. They provide structured data storage and methods for manipulating data for algorithms.
- Algorithms inject vitality into data structures. The data structure alone only stores data information; it is through the application of algorithms that specific problems can be solved.
- Algorithms can often be implemented based on different data structures, but their execution efficiency can vary greatly. Choosing the right data structure is key.
Figure 1-4 Relationship between data structures and algorithms
Data structures and algorithms can be likened to a set of building blocks, as illustrated in Figure 1-5. A building block set includes numerous pieces, accompanied by detailed assembly instructions. Following these instructions step by step allows us to construct an intricate block model.
Figure 1-5 Assembling blocks
The detailed correspondence between the two is shown in Table 1-1.
Table 1-1 Comparing data structures and algorithms to building blocks
| Data Structures and Algorithms | Building Blocks |
|---|---|
| Input data | Unassembled blocks |
| Data structure | Organization of blocks, including shape, size, connections, etc |
| Algorithm | A series of steps to assemble the blocks into the desired shape |
| Output data | Completed Block model |
It's worth noting that data structures and algorithms are independent of programming languages. For this reason, this book is able to provide implementations in multiple programming languages.
Conventional Abbreviation
In real-life discussions, we often refer to "Data Structures and Algorithms" simply as "Algorithms". For example, the well-known LeetCode algorithm questions actually test knowledge of both data structures and algorithms.