5.3 Double-ended queue¶
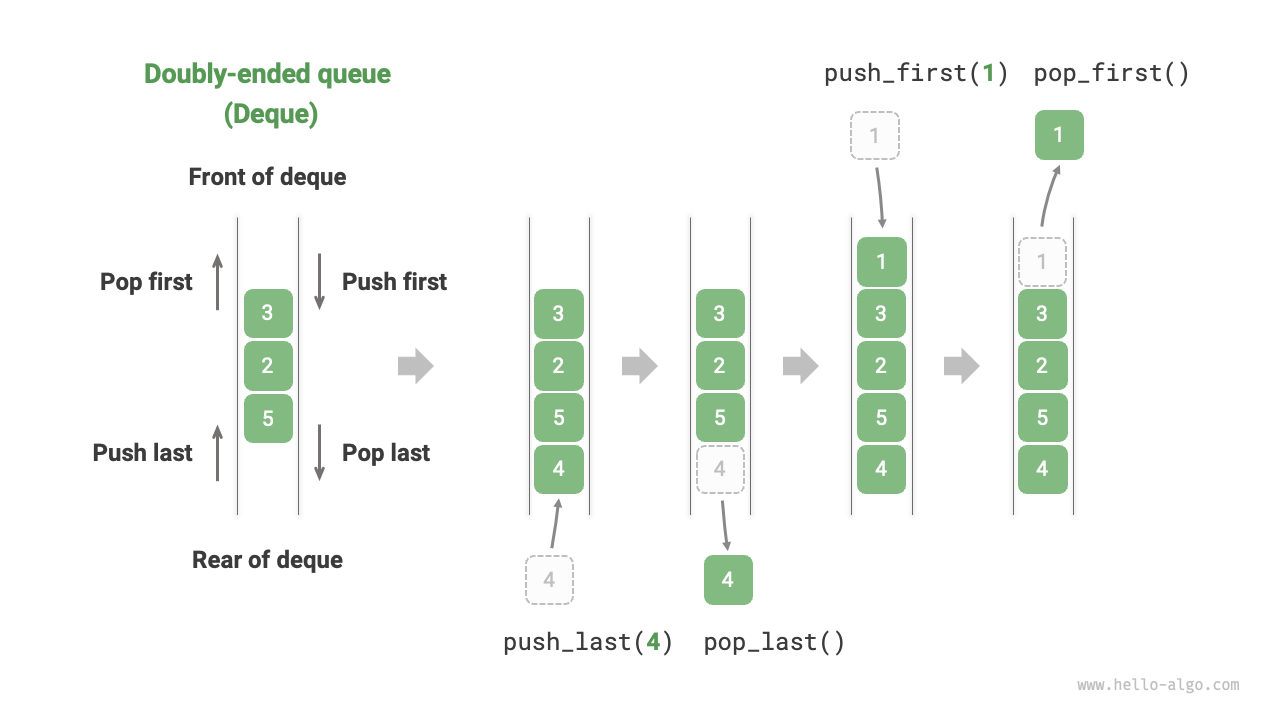
In a queue, we can only delete elements from the head or add elements to the tail. As shown in Figure 5-7, a double-ended queue (deque) offers more flexibility, allowing the addition or removal of elements at both the head and the tail.
Figure 5-7 Operations in double-ended queue
5.3.1 Common operations in double-ended queue¶
The common operations in a double-ended queue are listed below, and the names of specific methods depend on the programming language used.
Table 5-3 Efficiency of double-ended queue operations
| Method Name | Description | Time Complexity |
|---|---|---|
pushFirst() |
Add an element to the head | \(O(1)\) |
pushLast() |
Add an element to the tail | \(O(1)\) |
popFirst() |
Remove the first element | \(O(1)\) |
popLast() |
Remove the last element | \(O(1)\) |
peekFirst() |
Access the first element | \(O(1)\) |
peekLast() |
Access the last element | \(O(1)\) |
Similarly, we can directly use the double-ended queue classes implemented in programming languages:
from collections import deque
# Initialize the deque
deq: deque[int] = deque()
# Enqueue elements
deq.append(2) # Add to the tail
deq.append(5)
deq.append(4)
deq.appendleft(3) # Add to the head
deq.appendleft(1)
# Access elements
front: int = deq[0] # The first element
rear: int = deq[-1] # The last element
# Dequeue elements
pop_front: int = deq.popleft() # The first element dequeued
pop_rear: int = deq.pop() # The last element dequeued
# Get the length of the deque
size: int = len(deq)
# Check if the deque is empty
is_empty: bool = len(deq) == 0
/* Initialize the deque */
deque<int> deque;
/* Enqueue elements */
deque.push_back(2); // Add to the tail
deque.push_back(5);
deque.push_back(4);
deque.push_front(3); // Add to the head
deque.push_front(1);
/* Access elements */
int front = deque.front(); // The first element
int back = deque.back(); // The last element
/* Dequeue elements */
deque.pop_front(); // The first element dequeued
deque.pop_back(); // The last element dequeued
/* Get the length of the deque */
int size = deque.size();
/* Check if the deque is empty */
bool empty = deque.empty();
/* Initialize the deque */
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();
/* Enqueue elements */
deque.offerLast(2); // Add to the tail
deque.offerLast(5);
deque.offerLast(4);
deque.offerFirst(3); // Add to the head
deque.offerFirst(1);
/* Access elements */
int peekFirst = deque.peekFirst(); // The first element
int peekLast = deque.peekLast(); // The last element
/* Dequeue elements */
int popFirst = deque.pollFirst(); // The first element dequeued
int popLast = deque.pollLast(); // The last element dequeued
/* Get the length of the deque */
int size = deque.size();
/* Check if the deque is empty */
boolean isEmpty = deque.isEmpty();
/* Initialize the deque */
// In C#, LinkedList is used as a deque
LinkedList<int> deque = new();
/* Enqueue elements */
deque.AddLast(2); // Add to the tail
deque.AddLast(5);
deque.AddLast(4);
deque.AddFirst(3); // Add to the head
deque.AddFirst(1);
/* Access elements */
int peekFirst = deque.First.Value; // The first element
int peekLast = deque.Last.Value; // The last element
/* Dequeue elements */
deque.RemoveFirst(); // The first element dequeued
deque.RemoveLast(); // The last element dequeued
/* Get the length of the deque */
int size = deque.Count;
/* Check if the deque is empty */
bool isEmpty = deque.Count == 0;
/* Initialize the deque */
// In Go, use list as a deque
deque := list.New()
/* Enqueue elements */
deque.PushBack(2) // Add to the tail
deque.PushBack(5)
deque.PushBack(4)
deque.PushFront(3) // Add to the head
deque.PushFront(1)
/* Access elements */
front := deque.Front() // The first element
rear := deque.Back() // The last element
/* Dequeue elements */
deque.Remove(front) // The first element dequeued
deque.Remove(rear) // The last element dequeued
/* Get the length of the deque */
size := deque.Len()
/* Check if the deque is empty */
isEmpty := deque.Len() == 0
/* Initialize the deque */
// Swift does not have a built-in deque class, so Array can be used as a deque
var deque: [Int] = []
/* Enqueue elements */
deque.append(2) // Add to the tail
deque.append(5)
deque.append(4)
deque.insert(3, at: 0) // Add to the head
deque.insert(1, at: 0)
/* Access elements */
let peekFirst = deque.first! // The first element
let peekLast = deque.last! // The last element
/* Dequeue elements */
// Using Array, popFirst has a complexity of O(n)
let popFirst = deque.removeFirst() // The first element dequeued
let popLast = deque.removeLast() // The last element dequeued
/* Get the length of the deque */
let size = deque.count
/* Check if the deque is empty */
let isEmpty = deque.isEmpty
/* Initialize the deque */
// JavaScript does not have a built-in deque, so Array is used as a deque
const deque = [];
/* Enqueue elements */
deque.push(2);
deque.push(5);
deque.push(4);
// Note that unshift() has a time complexity of O(n) as it's an array
deque.unshift(3);
deque.unshift(1);
/* Access elements */
const peekFirst = deque[0]; // The first element
const peekLast = deque[deque.length - 1]; // The last element
/* Dequeue elements */
// Note that shift() has a time complexity of O(n) as it's an array
const popFront = deque.shift(); // The first element dequeued
const popBack = deque.pop(); // The last element dequeued
/* Get the length of the deque */
const size = deque.length;
/* Check if the deque is empty */
const isEmpty = size === 0;
/* Initialize the deque */
// TypeScript does not have a built-in deque, so Array is used as a deque
const deque: number[] = [];
/* Enqueue elements */
deque.push(2);
deque.push(5);
deque.push(4);
// Note that unshift() has a time complexity of O(n) as it's an array
deque.unshift(3);
deque.unshift(1);
/* Access elements */
const peekFirst: number = deque[0]; // The first element
const peekLast: number = deque[deque.length - 1]; // The last element
/* Dequeue elements */
// Note that shift() has a time complexity of O(n) as it's an array
const popFront: number = deque.shift() as number; // The first element dequeued
const popBack: number = deque.pop() as number; // The last element dequeued
/* Get the length of the deque */
const size: number = deque.length;
/* Check if the deque is empty */
const isEmpty: boolean = size === 0;
/* Initialize the deque */
// In Dart, Queue is defined as a deque
Queue<int> deque = Queue<int>();
/* Enqueue elements */
deque.addLast(2); // Add to the tail
deque.addLast(5);
deque.addLast(4);
deque.addFirst(3); // Add to the head
deque.addFirst(1);
/* Access elements */
int peekFirst = deque.first; // The first element
int peekLast = deque.last; // The last element
/* Dequeue elements */
int popFirst = deque.removeFirst(); // The first element dequeued
int popLast = deque.removeLast(); // The last element dequeued
/* Get the length of the deque */
int size = deque.length;
/* Check if the deque is empty */
bool isEmpty = deque.isEmpty;
/* Initialize the deque */
let mut deque: VecDeque<u32> = VecDeque::new();
/* Enqueue elements */
deque.push_back(2); // Add to the tail
deque.push_back(5);
deque.push_back(4);
deque.push_front(3); // Add to the head
deque.push_front(1);
/* Access elements */
if let Some(front) = deque.front() { // The first element
}
if let Some(rear) = deque.back() { // The last element
}
/* Dequeue elements */
if let Some(pop_front) = deque.pop_front() { // The first element dequeued
}
if let Some(pop_rear) = deque.pop_back() { // The last element dequeued
}
/* Get the length of the deque */
let size = deque.len();
/* Check if the deque is empty */
let is_empty = deque.is_empty();
Visualizing Code
https://pythontutor.com/render.html#code=from%20collections%20import%20deque%0A%0A%22%22%22Driver%20Code%22%22%22%0Aif%20__name__%20%3D%3D%20%22__main__%22%3A%0A%20%20%20%20%23%20%E5%88%9D%E5%A7%8B%E5%8C%96%E5%8F%8C%E5%90%91%E9%98%9F%E5%88%97%0A%20%20%20%20deq%20%3D%20deque%28%29%0A%0A%20%20%20%20%23%20%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0%E5%85%A5%E9%98%9F%0A%20%20%20%20deq.append%282%29%20%20%23%20%E6%B7%BB%E5%8A%A0%E8%87%B3%E9%98%9F%E5%B0%BE%0A%20%20%20%20deq.append%285%29%0A%20%20%20%20deq.append%284%29%0A%20%20%20%20deq.appendleft%283%29%20%20%23%20%E6%B7%BB%E5%8A%A0%E8%87%B3%E9%98%9F%E9%A6%96%0A%20%20%20%20deq.appendleft%281%29%0A%20%20%20%20print%28%22%E5%8F%8C%E5%90%91%E9%98%9F%E5%88%97%20deque%20%3D%22,%20deq%29%0A%0A%20%20%20%20%23%20%E8%AE%BF%E9%97%AE%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0%0A%20%20%20%20front%20%3D%20deq%5B0%5D%20%20%23%20%E9%98%9F%E9%A6%96%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0%0A%20%20%20%20print%28%22%E9%98%9F%E9%A6%96%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0%20front%20%3D%22,%20front%29%0A%20%20%20%20rear%20%3D%20deq%5B-1%5D%20%20%23%20%E9%98%9F%E5%B0%BE%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0%0A%20%20%20%20print%28%22%E9%98%9F%E5%B0%BE%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0%20rear%20%3D%22,%20rear%29%0A%0A%20%20%20%20%23%20%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0%E5%87%BA%E9%98%9F%0A%20%20%20%20pop_front%20%3D%20deq.popleft%28%29%20%20%23%20%E9%98%9F%E9%A6%96%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0%E5%87%BA%E9%98%9F%0A%20%20%20%20print%28%22%E9%98%9F%E9%A6%96%E5%87%BA%E9%98%9F%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0%20%20pop_front%20%3D%22,%20pop_front%29%0A%20%20%20%20print%28%22%E9%98%9F%E9%A6%96%E5%87%BA%E9%98%9F%E5%90%8E%20deque%20%3D%22,%20deq%29%0A%20%20%20%20pop_rear%20%3D%20deq.pop%28%29%20%20%23%20%E9%98%9F%E5%B0%BE%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0%E5%87%BA%E9%98%9F%0A%20%20%20%20print%28%22%E9%98%9F%E5%B0%BE%E5%87%BA%E9%98%9F%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0%20%20pop_rear%20%3D%22,%20pop_rear%29%0A%20%20%20%20print%28%22%E9%98%9F%E5%B0%BE%E5%87%BA%E9%98%9F%E5%90%8E%20deque%20%3D%22,%20deq%29%0A%0A%20%20%20%20%23%20%E8%8E%B7%E5%8F%96%E5%8F%8C%E5%90%91%E9%98%9F%E5%88%97%E7%9A%84%E9%95%BF%E5%BA%A6%0A%20%20%20%20size%20%3D%20len%28deq%29%0A%20%20%20%20print%28%22%E5%8F%8C%E5%90%91%E9%98%9F%E5%88%97%E9%95%BF%E5%BA%A6%20size%20%3D%22,%20size%29%0A%0A%20%20%20%20%23%20%E5%88%A4%E6%96%AD%E5%8F%8C%E5%90%91%E9%98%9F%E5%88%97%E6%98%AF%E5%90%A6%E4%B8%BA%E7%A9%BA%0A%20%20%20%20is_empty%20%3D%20len%28deq%29%20%3D%3D%200%0A%20%20%20%20print%28%22%E5%8F%8C%E5%90%91%E9%98%9F%E5%88%97%E6%98%AF%E5%90%A6%E4%B8%BA%E7%A9%BA%20%3D%22,%20is_empty%29&cumulative=false&curInstr=3&heapPrimitives=nevernest&mode=display&origin=opt-frontend.js&py=311&rawInputLstJSON=%5B%5D&textReferences=false
5.3.2 Implementing a double-ended queue *¶
The implementation of a double-ended queue is similar to that of a regular queue, it can be based on either a linked list or an array as the underlying data structure.
1. Implementation based on doubly linked list¶
Recall from the previous section that we used a regular singly linked list to implement a queue, as it conveniently allows for deleting from the head (corresponding to the dequeue operation) and adding new elements after the tail (corresponding to the enqueue operation).
For a double-ended queue, both the head and the tail can perform enqueue and dequeue operations. In other words, a double-ended queue needs to implement operations in the opposite direction as well. For this, we use a "doubly linked list" as the underlying data structure of the double-ended queue.
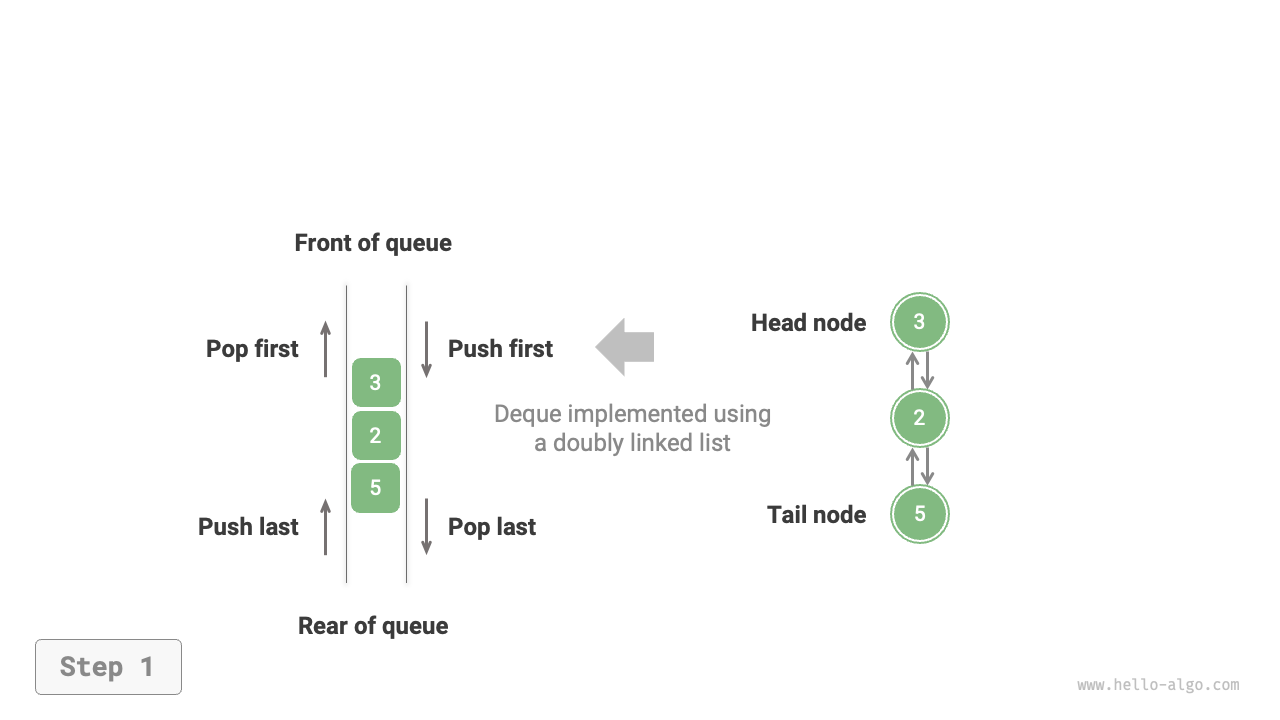
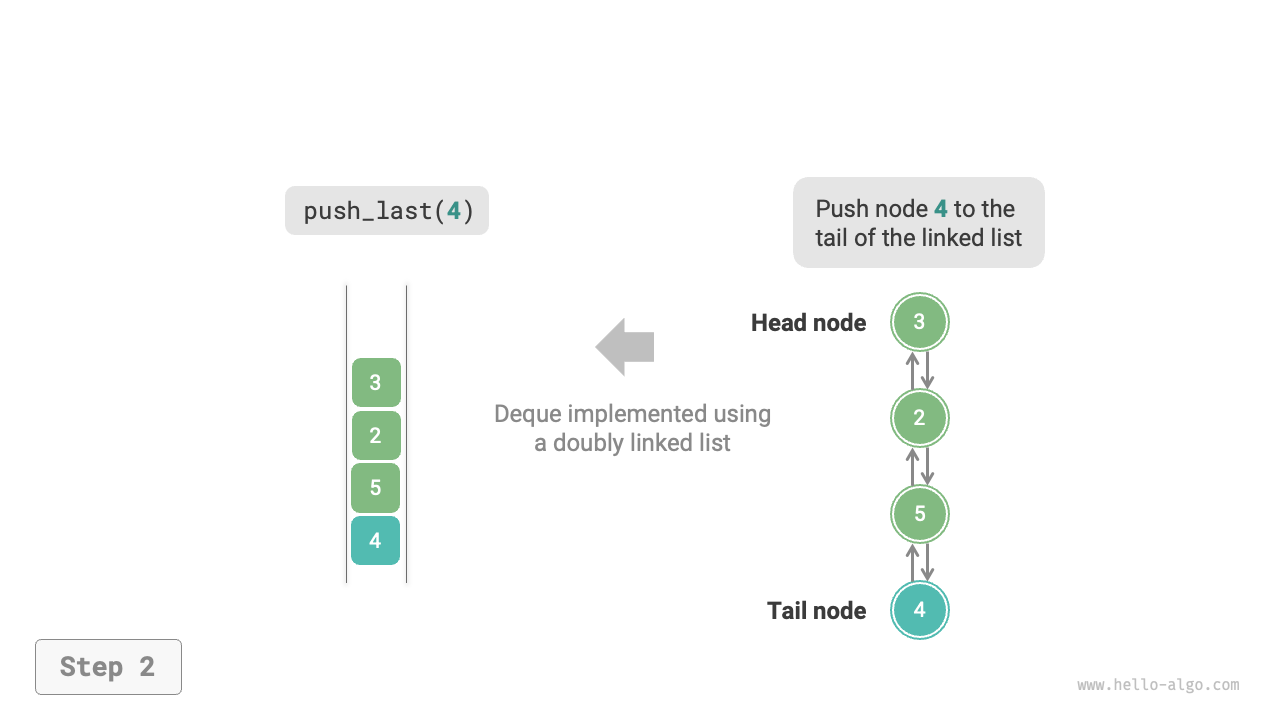
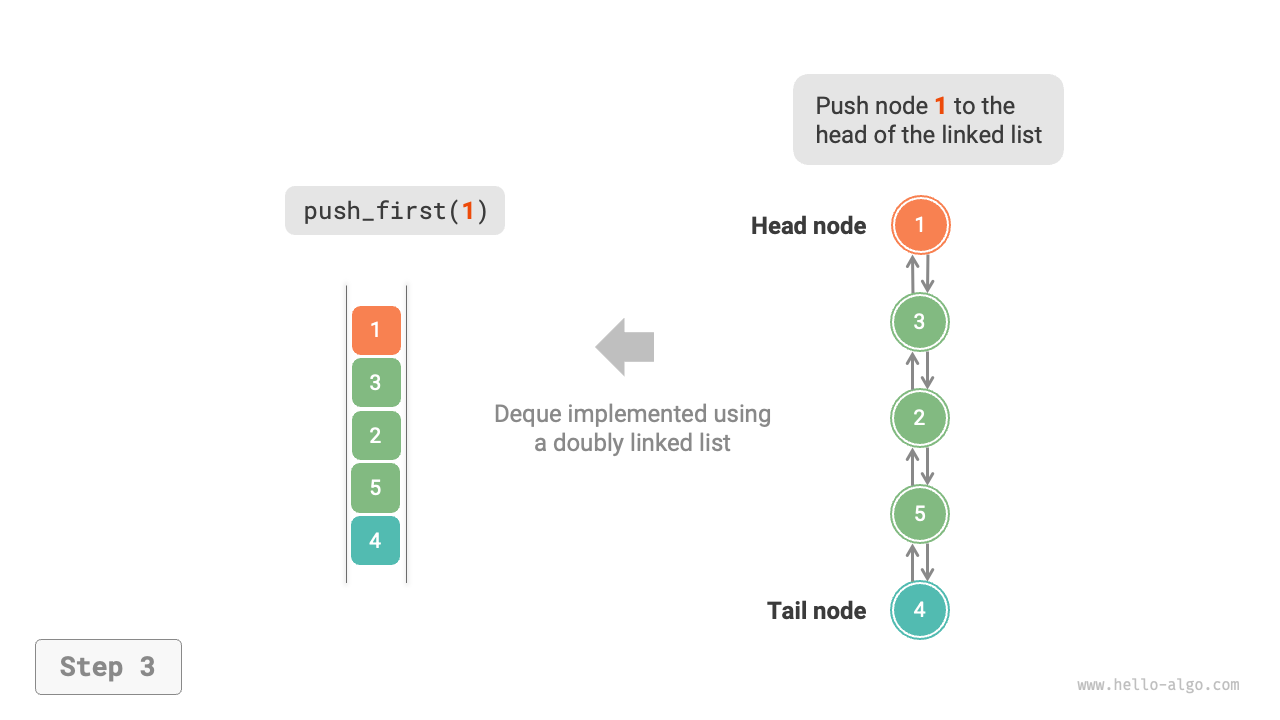
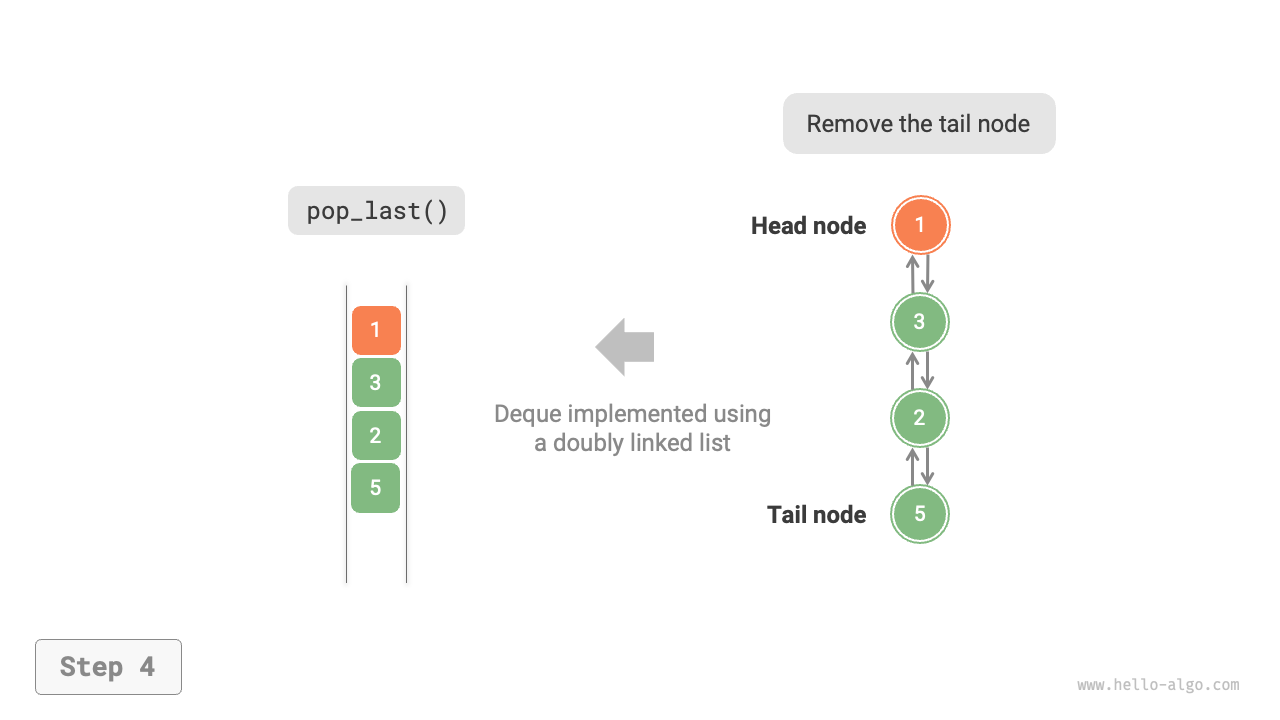
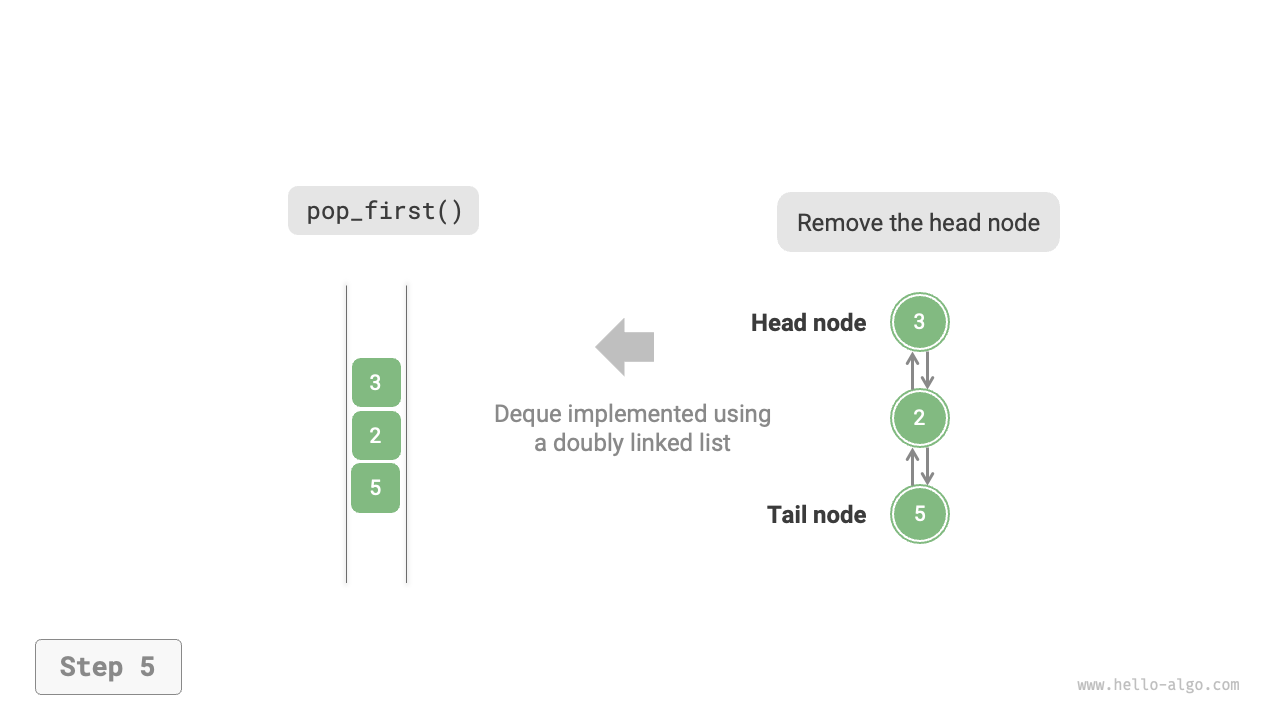
As shown in Figure 5-8, we treat the head and tail nodes of the doubly linked list as the front and rear of the double-ended queue, respectively, and implement the functionality to add and remove nodes at both ends.
Figure 5-8 Implementing Double-Ended Queue with Doubly Linked List for Enqueue and Dequeue Operations
The implementation code is as follows:
class ListNode:
"""Double-linked list node"""
def __init__(self, val: int):
"""Constructor"""
self.val: int = val
self.next: ListNode | None = None # Reference to successor node
self.prev: ListNode | None = None # Reference to predecessor node
class LinkedListDeque:
"""Double-ended queue class based on double-linked list"""
def __init__(self):
"""Constructor"""
self._front: ListNode | None = None # Head node front
self._rear: ListNode | None = None # Tail node rear
self._size: int = 0 # Length of the double-ended queue
def size(self) -> int:
"""Get the length of the double-ended queue"""
return self._size
def is_empty(self) -> bool:
"""Determine if the double-ended queue is empty"""
return self._size == 0
def push(self, num: int, is_front: bool):
"""Enqueue operation"""
node = ListNode(num)
# If the list is empty, make front and rear both point to node
if self.is_empty():
self._front = self._rear = node
# Front enqueue operation
elif is_front:
# Add node to the head of the list
self._front.prev = node
node.next = self._front
self._front = node # Update head node
# Rear enqueue operation
else:
# Add node to the tail of the list
self._rear.next = node
node.prev = self._rear
self._rear = node # Update tail node
self._size += 1 # Update queue length
def push_first(self, num: int):
"""Front enqueue"""
self.push(num, True)
def push_last(self, num: int):
"""Rear enqueue"""
self.push(num, False)
def pop(self, is_front: bool) -> int:
"""Dequeue operation"""
if self.is_empty():
raise IndexError("Double-ended queue is empty")
# Front dequeue operation
if is_front:
val: int = self._front.val # Temporarily store the head node value
# Remove head node
fnext: ListNode | None = self._front.next
if fnext is not None:
fnext.prev = None
self._front.next = None
self._front = fnext # Update head node
# Rear dequeue operation
else:
val: int = self._rear.val # Temporarily store the tail node value
# Remove tail node
rprev: ListNode | None = self._rear.prev
if rprev is not None:
rprev.next = None
self._rear.prev = None
self._rear = rprev # Update tail node
self._size -= 1 # Update queue length
return val
def pop_first(self) -> int:
"""Front dequeue"""
return self.pop(True)
def pop_last(self) -> int:
"""Rear dequeue"""
return self.pop(False)
def peek_first(self) -> int:
"""Access front element"""
if self.is_empty():
raise IndexError("Double-ended queue is empty")
return self._front.val
def peek_last(self) -> int:
"""Access rear element"""
if self.is_empty():
raise IndexError("Double-ended queue is empty")
return self._rear.val
def to_array(self) -> list[int]:
"""Return array for printing"""
node = self._front
res = [0] * self.size()
for i in range(self.size()):
res[i] = node.val
node = node.next
return res
/* Double-linked list node */
struct DoublyListNode {
int val; // Node value
DoublyListNode *next; // Pointer to successor node
DoublyListNode *prev; // Pointer to predecessor node
DoublyListNode(int val) : val(val), prev(nullptr), next(nullptr) {
}
};
/* Double-ended queue class based on double-linked list */
class LinkedListDeque {
private:
DoublyListNode *front, *rear; // Front node front, back node rear
int queSize = 0; // Length of the double-ended queue
public:
/* Constructor */
LinkedListDeque() : front(nullptr), rear(nullptr) {
}
/* Destructor */
~LinkedListDeque() {
// Traverse the linked list, remove nodes, free memory
DoublyListNode *pre, *cur = front;
while (cur != nullptr) {
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
delete pre;
}
}
/* Get the length of the double-ended queue */
int size() {
return queSize;
}
/* Determine if the double-ended queue is empty */
bool isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
/* Enqueue operation */
void push(int num, bool isFront) {
DoublyListNode *node = new DoublyListNode(num);
// If the list is empty, make front and rear both point to node
if (isEmpty())
front = rear = node;
// Front enqueue operation
else if (isFront) {
// Add node to the head of the list
front->prev = node;
node->next = front;
front = node; // Update head node
// Rear enqueue operation
} else {
// Add node to the tail of the list
rear->next = node;
node->prev = rear;
rear = node; // Update tail node
}
queSize++; // Update queue length
}
/* Front enqueue */
void pushFirst(int num) {
push(num, true);
}
/* Rear enqueue */
void pushLast(int num) {
push(num, false);
}
/* Dequeue operation */
int pop(bool isFront) {
if (isEmpty())
throw out_of_range("Queue is empty");
int val;
// Front dequeue operation
if (isFront) {
val = front->val; // Temporarily store the head node value
// Remove head node
DoublyListNode *fNext = front->next;
if (fNext != nullptr) {
fNext->prev = nullptr;
front->next = nullptr;
}
delete front;
front = fNext; // Update head node
// Rear dequeue operation
} else {
val = rear->val; // Temporarily store the tail node value
// Remove tail node
DoublyListNode *rPrev = rear->prev;
if (rPrev != nullptr) {
rPrev->next = nullptr;
rear->prev = nullptr;
}
delete rear;
rear = rPrev; // Update tail node
}
queSize--; // Update queue length
return val;
}
/* Front dequeue */
int popFirst() {
return pop(true);
}
/* Rear dequeue */
int popLast() {
return pop(false);
}
/* Access front element */
int peekFirst() {
if (isEmpty())
throw out_of_range("Double-ended queue is empty");
return front->val;
}
/* Access rear element */
int peekLast() {
if (isEmpty())
throw out_of_range("Double-ended queue is empty");
return rear->val;
}
/* Return array for printing */
vector<int> toVector() {
DoublyListNode *node = front;
vector<int> res(size());
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++) {
res[i] = node->val;
node = node->next;
}
return res;
}
};
/* Double-linked list node */
class ListNode {
int val; // Node value
ListNode next; // Reference to successor node
ListNode prev; // Reference to predecessor node
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
prev = next = null;
}
}
/* Double-ended queue class based on double-linked list */
class LinkedListDeque {
private ListNode front, rear; // Front node front, back node rear
private int queSize = 0; // Length of the double-ended queue
public LinkedListDeque() {
front = rear = null;
}
/* Get the length of the double-ended queue */
public int size() {
return queSize;
}
/* Determine if the double-ended queue is empty */
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
/* Enqueue operation */
private void push(int num, boolean isFront) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(num);
// If the list is empty, make front and rear both point to node
if (isEmpty())
front = rear = node;
// Front enqueue operation
else if (isFront) {
// Add node to the head of the list
front.prev = node;
node.next = front;
front = node; // Update head node
// Rear enqueue operation
} else {
// Add node to the tail of the list
rear.next = node;
node.prev = rear;
rear = node; // Update tail node
}
queSize++; // Update queue length
}
/* Front enqueue */
public void pushFirst(int num) {
push(num, true);
}
/* Rear enqueue */
public void pushLast(int num) {
push(num, false);
}
/* Dequeue operation */
private int pop(boolean isFront) {
if (isEmpty())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
int val;
// Front dequeue operation
if (isFront) {
val = front.val; // Temporarily store the head node value
// Remove head node
ListNode fNext = front.next;
if (fNext != null) {
fNext.prev = null;
front.next = null;
}
front = fNext; // Update head node
// Rear dequeue operation
} else {
val = rear.val; // Temporarily store the tail node value
// Remove tail node
ListNode rPrev = rear.prev;
if (rPrev != null) {
rPrev.next = null;
rear.prev = null;
}
rear = rPrev; // Update tail node
}
queSize--; // Update queue length
return val;
}
/* Front dequeue */
public int popFirst() {
return pop(true);
}
/* Rear dequeue */
public int popLast() {
return pop(false);
}
/* Access front element */
public int peekFirst() {
if (isEmpty())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
return front.val;
}
/* Access rear element */
public int peekLast() {
if (isEmpty())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
return rear.val;
}
/* Return array for printing */
public int[] toArray() {
ListNode node = front;
int[] res = new int[size()];
for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
res[i] = node.val;
node = node.next;
}
return res;
}
}
2. Implementation based on array¶
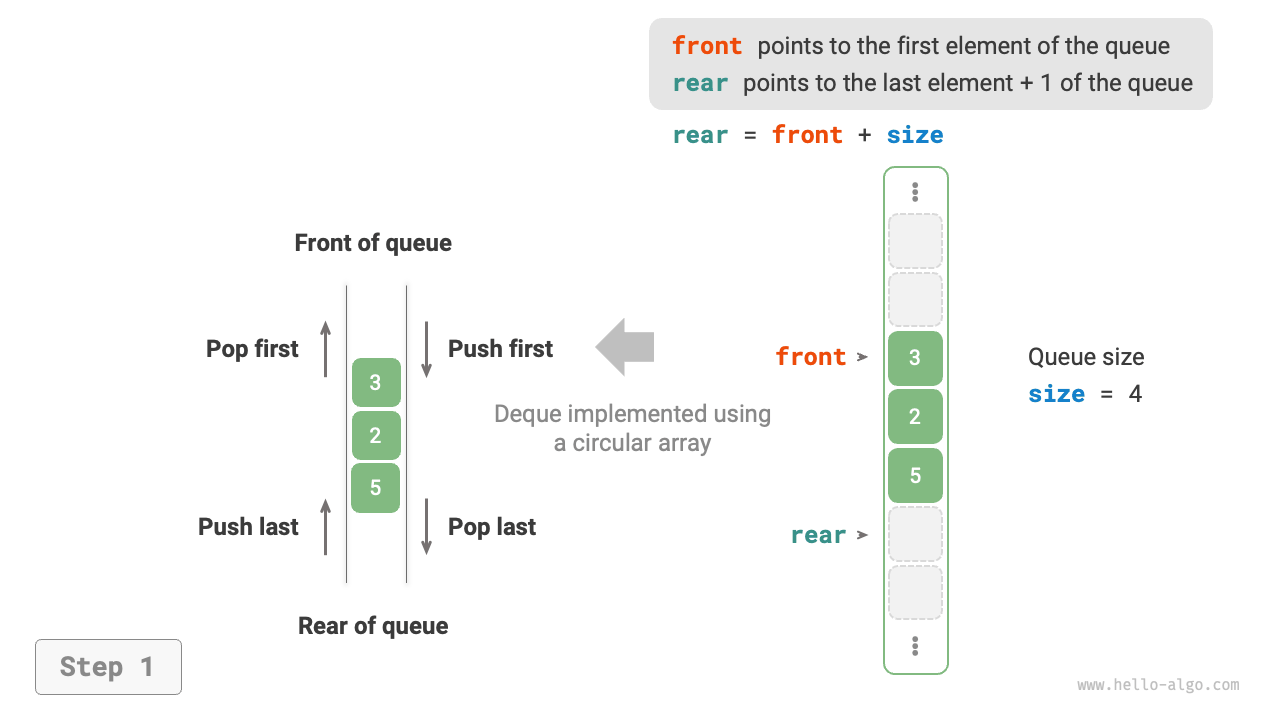
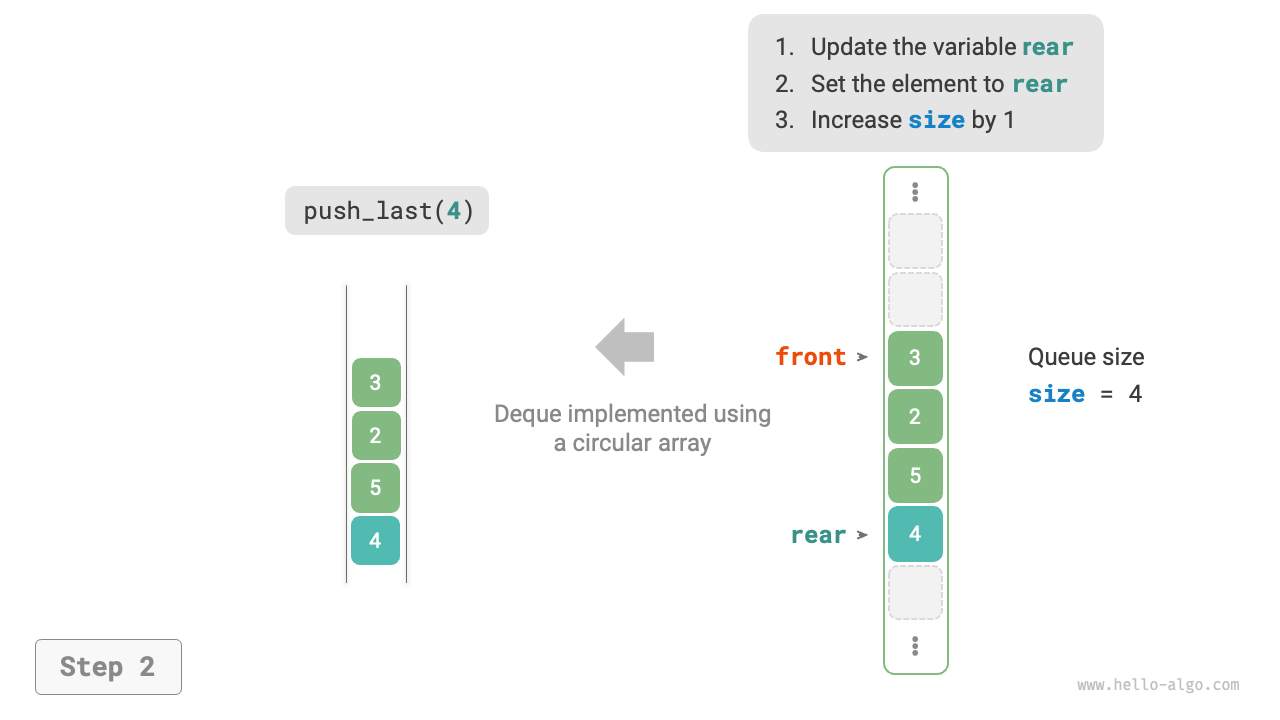
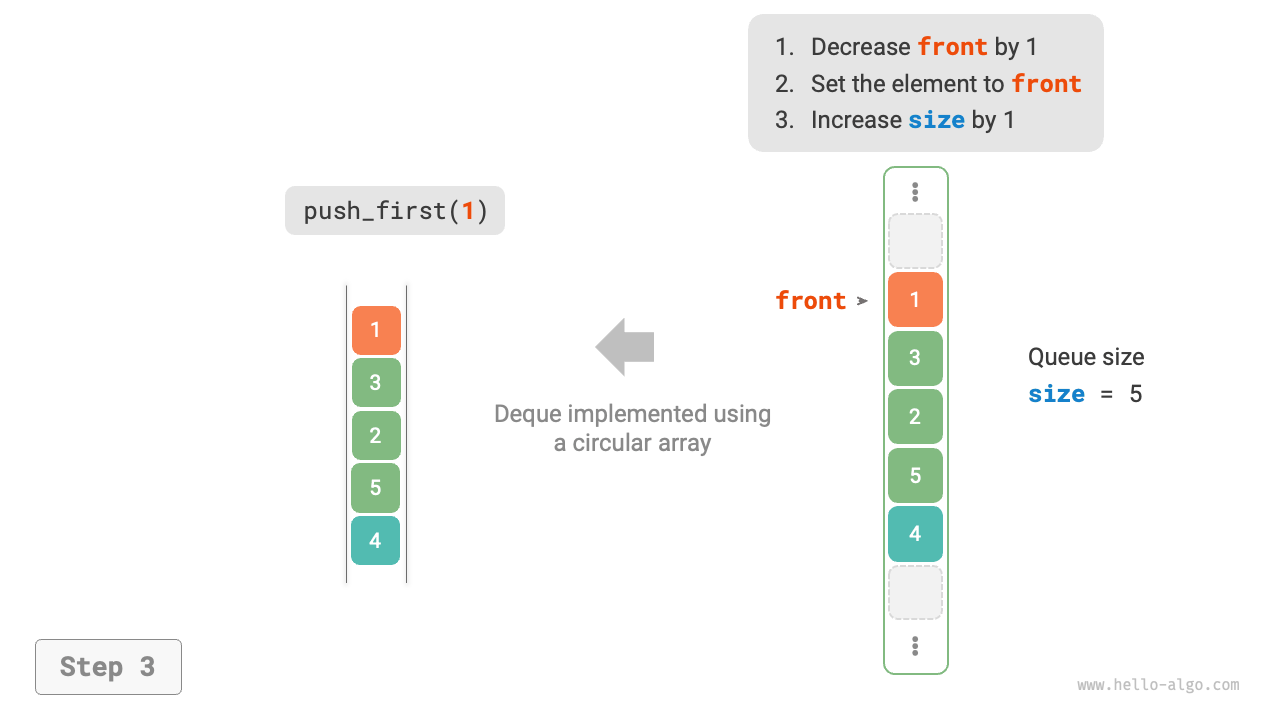
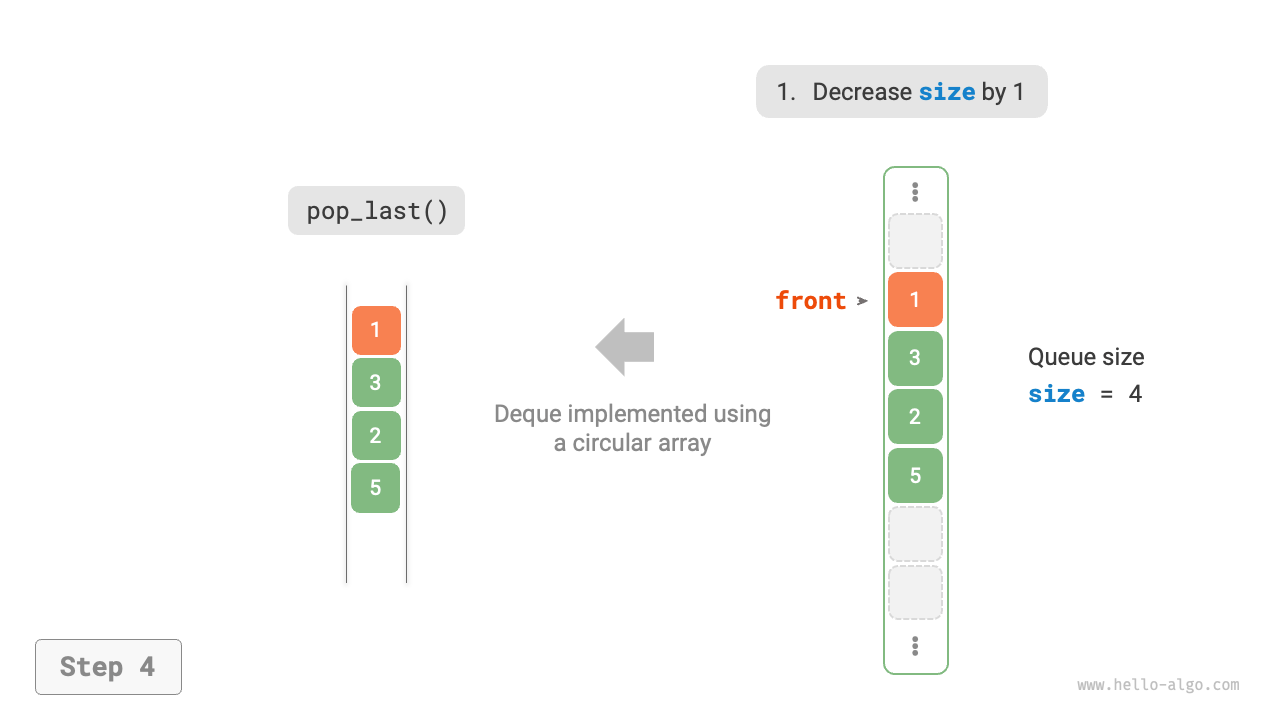
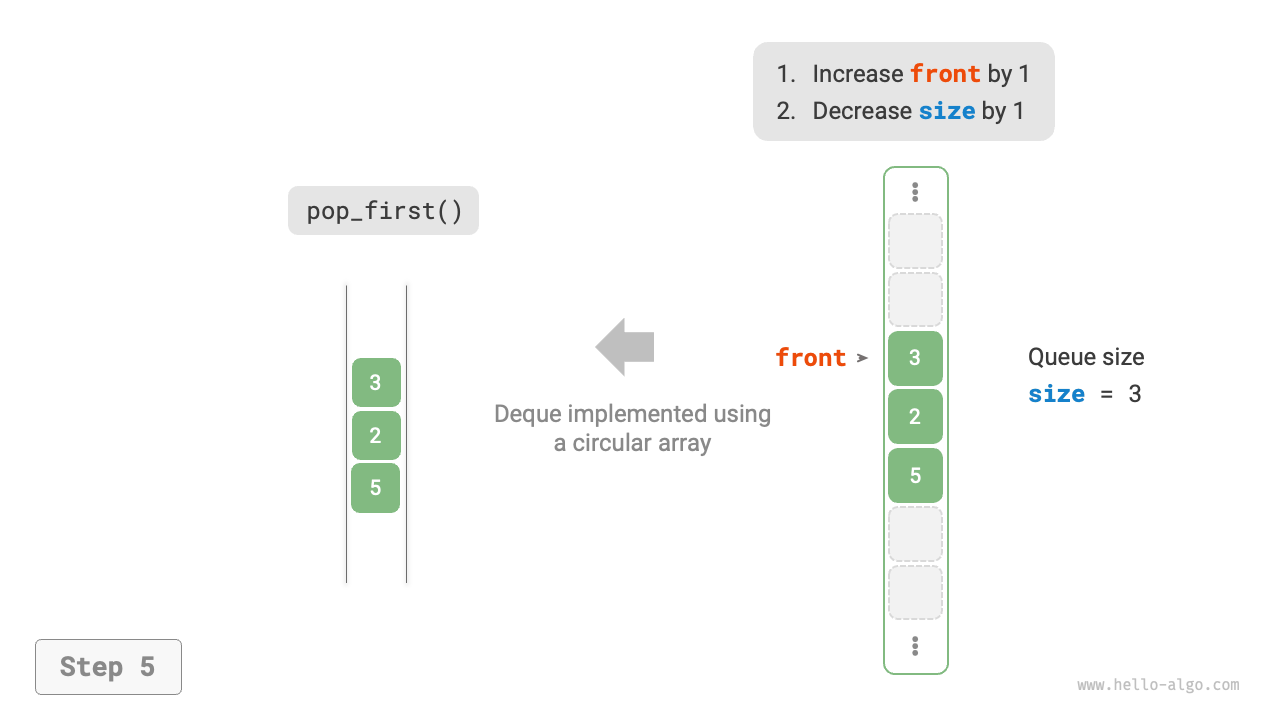
As shown in Figure 5-9, similar to implementing a queue with an array, we can also use a circular array to implement a double-ended queue.
Figure 5-9 Implementing Double-Ended Queue with Array for Enqueue and Dequeue Operations
The implementation only needs to add methods for "front enqueue" and "rear dequeue":
class ArrayDeque:
"""Double-ended queue class based on circular array"""
def __init__(self, capacity: int):
"""Constructor"""
self._nums: list[int] = [0] * capacity
self._front: int = 0
self._size: int = 0
def capacity(self) -> int:
"""Get the capacity of the double-ended queue"""
return len(self._nums)
def size(self) -> int:
"""Get the length of the double-ended queue"""
return self._size
def is_empty(self) -> bool:
"""Determine if the double-ended queue is empty"""
return self._size == 0
def index(self, i: int) -> int:
"""Calculate circular array index"""
# Implement circular array by modulo operation
# When i exceeds the tail of the array, return to the head
# When i exceeds the head of the array, return to the tail
return (i + self.capacity()) % self.capacity()
def push_first(self, num: int):
"""Front enqueue"""
if self._size == self.capacity():
print("Double-ended queue is full")
return
# Move the front pointer one position to the left
# Implement front crossing the head of the array to return to the tail by modulo operation
self._front = self.index(self._front - 1)
# Add num to the front
self._nums[self._front] = num
self._size += 1
def push_last(self, num: int):
"""Rear enqueue"""
if self._size == self.capacity():
print("Double-ended queue is full")
return
# Calculate rear pointer, pointing to rear index + 1
rear = self.index(self._front + self._size)
# Add num to the rear
self._nums[rear] = num
self._size += 1
def pop_first(self) -> int:
"""Front dequeue"""
num = self.peek_first()
# Move front pointer one position backward
self._front = self.index(self._front + 1)
self._size -= 1
return num
def pop_last(self) -> int:
"""Rear dequeue"""
num = self.peek_last()
self._size -= 1
return num
def peek_first(self) -> int:
"""Access front element"""
if self.is_empty():
raise IndexError("Double-ended queue is empty")
return self._nums[self._front]
def peek_last(self) -> int:
"""Access rear element"""
if self.is_empty():
raise IndexError("Double-ended queue is empty")
# Calculate rear element index
last = self.index(self._front + self._size - 1)
return self._nums[last]
def to_array(self) -> list[int]:
"""Return array for printing"""
# Only convert elements within valid length range
res = []
for i in range(self._size):
res.append(self._nums[self.index(self._front + i)])
return res
/* Double-ended queue class based on circular array */
class ArrayDeque {
private:
vector<int> nums; // Array used to store elements of the double-ended queue
int front; // Front pointer, pointing to the front element
int queSize; // Length of the double-ended queue
public:
/* Constructor */
ArrayDeque(int capacity) {
nums.resize(capacity);
front = queSize = 0;
}
/* Get the capacity of the double-ended queue */
int capacity() {
return nums.size();
}
/* Get the length of the double-ended queue */
int size() {
return queSize;
}
/* Determine if the double-ended queue is empty */
bool isEmpty() {
return queSize == 0;
}
/* Calculate circular array index */
int index(int i) {
// Implement circular array by modulo operation
// When i exceeds the tail of the array, return to the head
// When i exceeds the head of the array, return to the tail
return (i + capacity()) % capacity();
}
/* Front enqueue */
void pushFirst(int num) {
if (queSize == capacity()) {
cout << "Double-ended queue is full" << endl;
return;
}
// Move the front pointer one position to the left
// Implement front crossing the head of the array to return to the tail by modulo operation
front = index(front - 1);
// Add num to the front
nums[front] = num;
queSize++;
}
/* Rear enqueue */
void pushLast(int num) {
if (queSize == capacity()) {
cout << "Double-ended queue is full" << endl;
return;
}
// Calculate rear pointer, pointing to rear index + 1
int rear = index(front + queSize);
// Add num to the rear
nums[rear] = num;
queSize++;
}
/* Front dequeue */
int popFirst() {
int num = peekFirst();
// Move front pointer one position backward
front = index(front + 1);
queSize--;
return num;
}
/* Rear dequeue */
int popLast() {
int num = peekLast();
queSize--;
return num;
}
/* Access front element */
int peekFirst() {
if (isEmpty())
throw out_of_range("Double-ended queue is empty");
return nums[front];
}
/* Access rear element */
int peekLast() {
if (isEmpty())
throw out_of_range("Double-ended queue is empty");
// Calculate rear element index
int last = index(front + queSize - 1);
return nums[last];
}
/* Return array for printing */
vector<int> toVector() {
// Only convert elements within valid length range
vector<int> res(queSize);
for (int i = 0, j = front; i < queSize; i++, j++) {
res[i] = nums[index(j)];
}
return res;
}
};
/* Double-ended queue class based on circular array */
class ArrayDeque {
private int[] nums; // Array used to store elements of the double-ended queue
private int front; // Front pointer, pointing to the front element
private int queSize; // Length of the double-ended queue
/* Constructor */
public ArrayDeque(int capacity) {
this.nums = new int[capacity];
front = queSize = 0;
}
/* Get the capacity of the double-ended queue */
public int capacity() {
return nums.length;
}
/* Get the length of the double-ended queue */
public int size() {
return queSize;
}
/* Determine if the double-ended queue is empty */
public boolean isEmpty() {
return queSize == 0;
}
/* Calculate circular array index */
private int index(int i) {
// Implement circular array by modulo operation
// When i exceeds the tail of the array, return to the head
// When i exceeds the head of the array, return to the tail
return (i + capacity()) % capacity();
}
/* Front enqueue */
public void pushFirst(int num) {
if (queSize == capacity()) {
System.out.println("Double-ended queue is full");
return;
}
// Move the front pointer one position to the left
// Implement front crossing the head of the array to return to the tail by modulo operation
front = index(front - 1);
// Add num to the front
nums[front] = num;
queSize++;
}
/* Rear enqueue */
public void pushLast(int num) {
if (queSize == capacity()) {
System.out.println("Double-ended queue is full");
return;
}
// Calculate rear pointer, pointing to rear index + 1
int rear = index(front + queSize);
// Add num to the rear
nums[rear] = num;
queSize++;
}
/* Front dequeue */
public int popFirst() {
int num = peekFirst();
// Move front pointer one position backward
front = index(front + 1);
queSize--;
return num;
}
/* Rear dequeue */
public int popLast() {
int num = peekLast();
queSize--;
return num;
}
/* Access front element */
public int peekFirst() {
if (isEmpty())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
return nums[front];
}
/* Access rear element */
public int peekLast() {
if (isEmpty())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
// Calculate rear element index
int last = index(front + queSize - 1);
return nums[last];
}
/* Return array for printing */
public int[] toArray() {
// Only convert elements within valid length range
int[] res = new int[queSize];
for (int i = 0, j = front; i < queSize; i++, j++) {
res[i] = nums[index(j)];
}
return res;
}
}
5.3.3 Applications of double-ended queue¶
The double-ended queue combines the logic of both stacks and queues, thus, it can implement all their respective use cases while offering greater flexibility.
We know that software's "undo" feature is typically implemented using a stack: the system pushes each change operation onto the stack and then pops to implement undoing. However, considering the limitations of system resources, software often restricts the number of undo steps (for example, only allowing the last 50 steps). When the stack length exceeds 50, the software needs to perform a deletion operation at the bottom of the stack (the front of the queue). But a regular stack cannot perform this function, where a double-ended queue becomes necessary. Note that the core logic of "undo" still follows the Last-In-First-Out principle of a stack, but a double-ended queue can more flexibly implement some additional logic.